Logging¶
- Autor
Vinay Sajip <vinay_sajip at red-dove dot com>
Tutorial Básico de Logging¶
Logging é uma maneira de rastrear eventos que acontecem quando algum software executa. O desenvolvedor de software adiciona chamadas de logging no código para indicar que determinado evento ocorreu. Um evento é descrito por uma mensagem descritiva que pode opcionalmente conter o dado de uma variável (ex.: dado que é potencialmente diferente pra cada ocorrência do evento). Eventos também tem um peso que o desenvolvedor atribui para o evento; o peso pode também ser chamada de níveis ou severidade.
Quando usar logging¶
Logging provê um conjunto de funções convenientes para o uso simples de logging. Estas funções são debug(), info(), warning(), error() and critical(). Para determinar quando usar logging, consulte a tabela abaixo, qual estado, para cada conjunto de tarefas comuns, qual a melhor ferramenta para usar.
Tarefa que você quer performar |
A melhor ferramenta para a tarefa |
|---|---|
Exibir saída do console para uso ordinário de um script de linha de comando ou programa. |
|
Relata eventos que podem ocorrer durante a operação normal de um programa (ex: para monitoramento do status ou investigação de falha) |
|
Emite um aviso sobre um evento de tempo de execução específico |
|
Relata um erro sobre um evento de tempo de execução específico |
Levantando uma exceção |
Relatar supressão de um erro sem levantar uma exceção (ex: manipulador de erros em um processo de servidor em longa execução) |
|
As funções logging são nomeadas por nível ou severidade dos eventos que eles costumam rastrear. Os níveis padrões e suas aplicações são descritas abaixo (em ordem crescente de severidade):
Nível |
Quando é usado |
|---|---|
|
Informação detalhada, tipicamente de interesse apenas quando diagnosticando problemas. |
|
Confirmação de que as coisas estão funcionando como esperado. |
|
Uma indicação que algo inesperado aconteceu, ou um indicativo que algum problema em um futuro próximo (ex.: ‘pouco espaço em disco’). O software está ainda funcionando como esperado. |
|
Por conta de um problema mais grave, o software não conseguiu executar alguma função. |
|
Um erro grave, indicando que o programa pode não conseguir continuar rodando. |
O nível padrão é WARNING, que significa que só eventos deste nível e acima serão rastreados, a não ser que o pacote logging esteja configurado para fazer de outra forma.
Eventos que são rastreados podem ser tratados de diferentes formas. O jeito mais simples de lidar com eventos rastreados é exibi-los no console. Outra maneira comum é gravá-los em um arquivo de disco.
Um exemplo simples¶
Um exemplo bastante simples é:
import logging
logging.warning('Watch out!') # will print a message to the console
logging.info('I told you so') # will not print anything
Se você digitar essas linhas no script e executá-lo, você verá:
WARNING:root:Watch out!
exibido no console. A mensagem INFO não aparece porque o nível padrão é WARNING. A mensagem exibida inclui a indicação do nível e uma descrição do evento informado na chamada ao logging, ex.: “Cuidado!”. Não se preocupe sobre entender tudo agora. Isto será explicado mais tarde. A saída pode ser formatada de forma bastante flexível se você precisar; opções de formatação serão também explicadas posteriormente.
Logging em um arquivo¶
Um situação bem comum é gravar os eventos de logging em um arquivo, portanto vamos dar um olhada nisto na sequência. Tenha certeza de tentar os seguintes comandos em um novo interpretador Python, e não apenas continuar da sessão que foi descrita acima:
import logging
logging.basicConfig(filename='example.log',level=logging.DEBUG)
logging.debug('This message should go to the log file')
logging.info('So should this')
logging.warning('And this, too')
E agora se nós abrirmos o arquivo e olharmos o que temos, deveremos encontrar essas mensagens de log:
DEBUG:root:This message should go to the log file
INFO:root:So should this
WARNING:root:And this, too
Este exemplo também mostra como você pode configurar o nível do logging que age como um limiar para o rastreamento. Neste caso, por causa que definimos o limiar como DEBUG, todas as mensagens foram exibidas.
Se você quer definir o nível de logging a partir de uma opção da linha de comando como:
--log=INFO
e você tem o valor do parâmetro passado pelo --log em alguma variável loglevel, você pode usar:
getattr(logging, loglevel.upper())
para obter o valor que você passará para a basicConfig() via o level argumento. Você pode querer verificar qualquer erros introduzidos pelo usuário, talvez como no exemplo a seguir:
# assuming loglevel is bound to the string value obtained from the
# command line argument. Convert to upper case to allow the user to
# specify --log=DEBUG or --log=debug
numeric_level = getattr(logging, loglevel.upper(), None)
if not isinstance(numeric_level, int):
raise ValueError('Invalid log level: %s' % loglevel)
logging.basicConfig(level=numeric_level, ...)
A chamada a basicConfig() deve vir antes de qualquer chamada para debug(), info() etc. Como isto pretende ser um simples facilitador de configuração, apenas a primeira chamada irá realmente fazer algo: As próximas chamadas não serão efetivamente operacionais.
Se você executar o script acima diversas vezes, as mensagens das sucessivas execuções serão acrescentadas ao arquivo example.log. Se você quer que cada execução seja iniciada novamente, não guardando as mensagens das execuções anteriores, você pode especificar o filemode argumento, mudando a chamada no exemplo acima:
logging.basicConfig(filename='example.log', filemode='w', level=logging.DEBUG)
A saída será a mesma de antes, mas o arquivo de log não será mais incrementado, desta forma as mensagens de execuções anteriores serão perdidas.
Logging de múltiplos módulos¶
Se seu programa tem múltiplos módulos, aqui está um exemplo de como você pode organizar o logging nele:
# myapp.py
import logging
import mylib
def main():
logging.basicConfig(filename='myapp.log', level=logging.INFO)
logging.info('Started')
mylib.do_something()
logging.info('Finished')
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
# mylib.py
import logging
def do_something():
logging.info('Doing something')
Se você executar myapp.py, deverá ver isso em myapp.log:
INFO:root:Started
INFO:root:Doing something
INFO:root:Finished
que é com sorte o que você espera ver. Você pode generalizar isto para múltiplos módulos, usando o padrão da mylib.py. Note que para este uso deste simples padrão, você não saberá, olhando no arquivo de log, onde na sua aplicação suas mensagens vieram, independente de olhar a descrição do evento. Se você quer rastrear a localização das suas mensagens, você precisará consultar a documentação além do tutorial de níveis – veja Tutorial Avançado do Logging.
Logging dados de uma variável¶
Para logar o dado de uma variável, use o formato string para a mensagem descritiva do evento e adicione a variável como argumento. Exemplo:
import logging
logging.warning('%s before you %s', 'Look', 'leap!')
exibirá:
WARNING:root:Look before you leap!
Como você pode ver, para combinar uma variável de dados na mensagem descritiva do evento usamos o velho, %-s estilo de formatação de string. Isto é usado para garantir compatibilidade com as versões anteriores: o pacote logging pré-data novas opções de formatação como str.format() e string.Template. Estas novas opções de formatação são suportadas, mas explorá-las esta fora do escopo deste tutorial: veja Using particular formatting styles throughout your application para mais informações.
Alterar o formato das mensagens exibidas¶
Para mudar o formato usado para exibir mensagens, você precisa especificar o formato que quer usar:
import logging
logging.basicConfig(format='%(levelname)s:%(message)s', level=logging.DEBUG)
logging.debug('This message should appear on the console')
logging.info('So should this')
logging.warning('And this, too')
que vai exibir:
DEBUG:This message should appear on the console
INFO:So should this
WARNING:And this, too
Note que a palavra ‘root’ que apareceu nos exemplos anteriores desapareceu. Para todas as configurações que possam aparecer na formatação de strings, você pode consultar a documentação Atributos LogRecord, mas para uso simples, você só precisa do levelname (severidade), message (descrição do evento, incluindo a variável com dados) e talvez exibir quando o evento ocorreu. Isto esta descrito na próxima seção.
Exibindo data/hora em mensagens¶
Para exibir a data e hora de um evento, você pode colocar ‘%(asctime)s’ no seu formato string:
import logging
logging.basicConfig(format='%(asctime)s %(message)s')
logging.warning('is when this event was logged.')
que deve exibir algo assim:
2010-12-12 11:41:42,612 is when this event was logged.
O formato padrão para data/hora (mostrado abaixo) é como a ISO8601 ou RFC 3339. Se você precisa de mais controle sobre a formatação de data/hora, informe o datefmt argumento para basicConfig, como neste exemplo:
import logging
logging.basicConfig(format='%(asctime)s %(message)s', datefmt='%m/%d/%Y %I:%M:%S %p')
logging.warning('is when this event was logged.')
que deve exibir algo assim:
12/12/2010 11:46:36 AM is when this event was logged.
O formato do argumento datefmt é o mesmo suportado por time.strftime().
Próximos Passos¶
Concluímos aqui o tutorial básico. Isto deve ser o bastante para você começar a trabalhar com logging. Existe muito mais que o pacote de logging pode oferecer, mas para ter o melhor disto, você precisará investir um pouco mais do seu tempo lendo as próximas seções. Se você está pronto para isso, pegue sua bebida favorita e continue.
Se sua necessidade de logging é simples, então use os exemplos acima para incorporar o logging nos seus scripts, se você encontrar algum problema ou não entender algo, por favor envie um pergunta no comp.lang.python Usenet grupo (disponível no https://groups.google.com/forum/#!forum/comp.lang.python) e você deverá receber ajuda assim que possível.
Ainda por aqui? Você pode continuar lendo as seções seguintes, que tem um tutorial mais avançado que o básico acima. Depois disso, você pode dar uma olhada no Livro de Receitas do Logging.
Tutorial Avançado do Logging¶
A biblioteca de logging tem uma abordagem modular e oferece algumas categorias de componentes: loggers, handlers, filters, e formatters.
Loggers expõem a interface que o código da aplicação usa diretamente.
Handlers enviam os registros do evento (criados por loggers) aos destinos apropriados.
Filters fornecem uma facilidade granular para determinar quais registros de eventos enviar à saída.
Formatters especificam o layout dos registros de eventos na saída final.
Uma informação de um evento de log é passada entre loggers, handlers, filters e formatters em uma instância de uma LogRecord
Logging é executada chamando métodos nas instâncias da Logger classe, também chamado de loggers. Cada instância tem um nome, e eles são conceitualmente organizados em uma hierarquia de espaço de nomes usando pontos como separadores. Por exemplo, um logger nomeado com ‘scan’ é o pai do logger ‘scan.text’, ‘scan.html’ e ‘scan.pdf’. Você pode nomear o logger do jeito que preferir, e indicar a área de uma aplicação em que uma mensagem de log origina.
Uma boa convenção para usar quando nomear loggers é usar um módulo-nível logger, em cada módulo que usa o logging, nomeado como sugerido abaixo:
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
Isto significa que o nome de um logger rastreia a hierarquia do pacote/módulo, e isto é obviamente intuitivo onde os eventos estão sendo registrados apenas pelo nome do logger.
The root of the hierarchy of loggers is called the root logger. That’s the
logger used by the functions debug(), info(), warning(),
error() and critical(), which just call the same-named method of
the root logger. The functions and the methods have the same signatures. The
root logger’s name is printed as ‘root’ in the logged output.
It is, of course, possible to log messages to different destinations. Support is included in the package for writing log messages to files, HTTP GET/POST locations, email via SMTP, generic sockets, queues, or OS-specific logging mechanisms such as syslog or the Windows NT event log. Destinations are served by handler classes. You can create your own log destination class if you have special requirements not met by any of the built-in handler classes.
By default, no destination is set for any logging messages. You can specify
a destination (such as console or file) by using basicConfig() as in the
tutorial examples. If you call the functions debug(), info(),
warning(), error() and critical(), they will check to see
if no destination is set; and if one is not set, they will set a destination
of the console (sys.stderr) and a default format for the displayed
message before delegating to the root logger to do the actual message output.
O formato padrão definido por basicConfig() para mensagens é:
severity:logger name:message
You can change this by passing a format string to basicConfig() with the
format keyword argument. For all options regarding how a format string is
constructed, see Formatter Objects.
Fluxo de Logging¶
O fluxo dos eventos de log em loggers e handlers é ilustrado no diagrama a seguir.
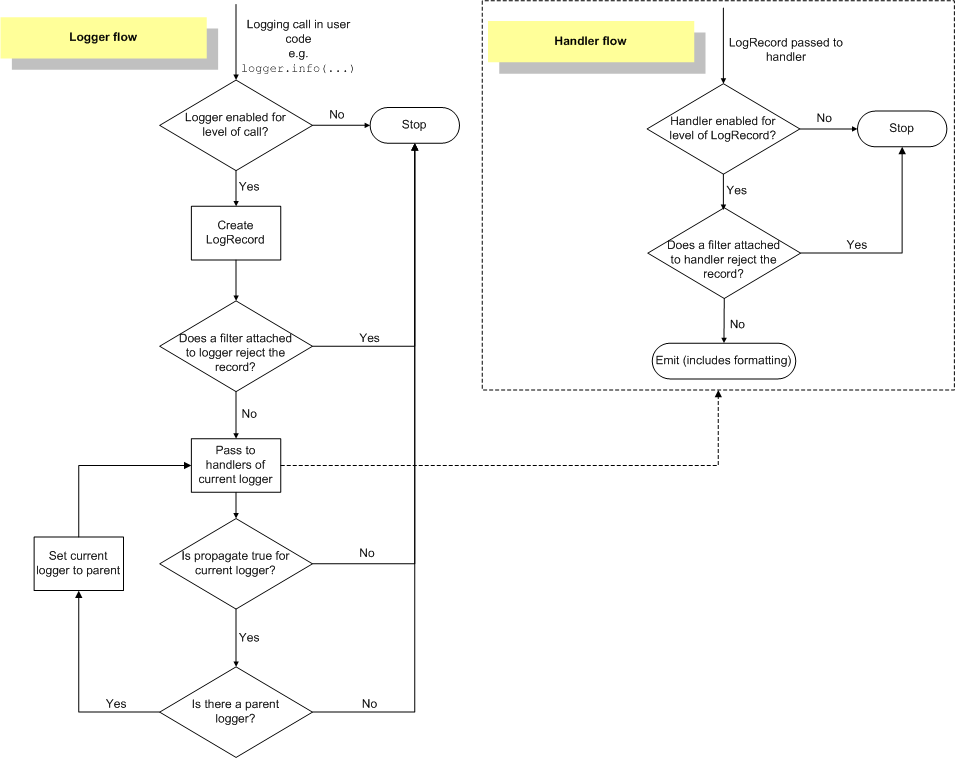
Registradores¶
Logger objects have a threefold job. First, they expose several
methods to application code so that applications can log messages at runtime.
Second, logger objects determine which log messages to act upon based upon
severity (the default filtering facility) or filter objects. Third, logger
objects pass along relevant log messages to all interested log handlers.
Os métodos mais usados em objetos logger se enquadram em duas categorias: configuração e envio de mensagem.
Esses são os métodos de configuração mais comuns:
Logger.setLevel()specifies the lowest-severity log message a logger will handle, where debug is the lowest built-in severity level and critical is the highest built-in severity. For example, if the severity level is INFO, the logger will handle only INFO, WARNING, ERROR, and CRITICAL messages and will ignore DEBUG messages.Logger.addHandler()andLogger.removeHandler()add and remove handler objects from the logger object. Handlers are covered in more detail in Manipuladores.Logger.addFilter()andLogger.removeFilter()add and remove filter objects from the logger object. Filters are covered in more detail in Filter Objects.
Você não precisa sempre invocar esses métodos em cada logger que criar. Veja os últimos dois paragrafos nessa seção.
Com o objeto logger configurado, os seguintes métodos criam mensagens de log:
Logger.debug(),Logger.info(),Logger.warning(),Logger.error(), andLogger.critical()all create log records with a message and a level that corresponds to their respective method names. The message is actually a format string, which may contain the standard string substitution syntax of%s,%d,%f, and so on. The rest of their arguments is a list of objects that correspond with the substitution fields in the message. With regard to**kwargs, the logging methods care only about a keyword ofexc_infoand use it to determine whether to log exception information.Logger.exception()creates a log message similar toLogger.error(). The difference is thatLogger.exception()dumps a stack trace along with it. Call this method only from an exception handler.Logger.log()takes a log level as an explicit argument. This is a little more verbose for logging messages than using the log level convenience methods listed above, but this is how to log at custom log levels.
getLogger() returns a reference to a logger instance with the specified
name if it is provided, or root if not. The names are period-separated
hierarchical structures. Multiple calls to getLogger() with the same name
will return a reference to the same logger object. Loggers that are further
down in the hierarchical list are children of loggers higher up in the list.
For example, given a logger with a name of foo, loggers with names of
foo.bar, foo.bar.baz, and foo.bam are all descendants of foo.
Loggers have a concept of effective level. If a level is not explicitly set
on a logger, the level of its parent is used instead as its effective level.
If the parent has no explicit level set, its parent is examined, and so on -
all ancestors are searched until an explicitly set level is found. The root
logger always has an explicit level set (WARNING by default). When deciding
whether to process an event, the effective level of the logger is used to
determine whether the event is passed to the logger’s handlers.
Child loggers propagate messages up to the handlers associated with their
ancestor loggers. Because of this, it is unnecessary to define and configure
handlers for all the loggers an application uses. It is sufficient to
configure handlers for a top-level logger and create child loggers as needed.
(You can, however, turn off propagation by setting the propagate
attribute of a logger to False.)
Manipuladores¶
Handler objects are responsible for dispatching the
appropriate log messages (based on the log messages’ severity) to the handler’s
specified destination. Logger objects can add zero or more handler
objects to themselves with an addHandler() method. As an example
scenario, an application may want to send all log messages to a log file, all
log messages of error or higher to stdout, and all messages of critical to an
email address. This scenario requires three individual handlers where each
handler is responsible for sending messages of a specific severity to a specific
location.
A biblioteca padrão possui alguns tipos de handler (veja Useful Handlers); os tutoriais usam principalmente StreamHandler e FileHandler nos seus exemplos.
There are very few methods in a handler for application developers to concern themselves with. The only handler methods that seem relevant for application developers who are using the built-in handler objects (that is, not creating custom handlers) are the following configuration methods:
The
setLevel()method, just as in logger objects, specifies the lowest severity that will be dispatched to the appropriate destination. Why are there twosetLevel()methods? The level set in the logger determines which severity of messages it will pass to its handlers. The level set in each handler determines which messages that handler will send on.setFormatter()selects a Formatter object for this handler to use.addFilter()andremoveFilter()respectively configure and deconfigure filter objects on handlers.
Application code should not directly instantiate and use instances of
Handler. Instead, the Handler class is a base class that
defines the interface that all handlers should have and establishes some
default behavior that child classes can use (or override).
Formatadores¶
Formatter objects configure the final order, structure, and contents of the log
message. Unlike the base logging.Handler class, application code may
instantiate formatter classes, although you could likely subclass the formatter
if your application needs special behavior. The constructor takes three
optional arguments – a message format string, a date format string and a style
indicator.
-
logging.Formatter.__init__(fmt=None, datefmt=None, style='%')¶
If there is no message format string, the default is to use the raw message. If there is no date format string, the default date format is:
%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S
with the milliseconds tacked on at the end. The style is one of %, ‘{’
or ‘$’. If one of these is not specified, then ‘%’ will be used.
If the style is ‘%’, the message format string uses
%(<dictionary key>)s styled string substitution; the possible keys are
documented in Atributos LogRecord. If the style is ‘{’, the message
format string is assumed to be compatible with str.format() (using
keyword arguments), while if the style is ‘$’ then the message format string
should conform to what is expected by string.Template.substitute().
Alterado na versão 3.2: Adicionado o parâmetro style.
A string de formato a seguir vai escrever o tempo em um formato légivel para humanos, a severidade da mensagem, e o conteúdo da mensagem, nessa ordem:
'%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s'
Formatters use a user-configurable function to convert the creation time of a
record to a tuple. By default, time.localtime() is used; to change this
for a particular formatter instance, set the converter attribute of the
instance to a function with the same signature as time.localtime() or
time.gmtime(). To change it for all formatters, for example if you want
all logging times to be shown in GMT, set the converter attribute in the
Formatter class (to time.gmtime for GMT display).
Configurando Logging¶
Programadores podem configurar logging de três formas:
Creating loggers, handlers, and formatters explicitly using Python code that calls the configuration methods listed above.
Creating a logging config file and reading it using the
fileConfig()function.Creating a dictionary of configuration information and passing it to the
dictConfig()function.
For the reference documentation on the last two options, see Configuration functions. The following example configures a very simple logger, a console handler, and a simple formatter using Python code:
import logging
# create logger
logger = logging.getLogger('simple_example')
logger.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
# create console handler and set level to debug
ch = logging.StreamHandler()
ch.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
# create formatter
formatter = logging.Formatter('%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')
# add formatter to ch
ch.setFormatter(formatter)
# add ch to logger
logger.addHandler(ch)
# 'application' code
logger.debug('debug message')
logger.info('info message')
logger.warning('warn message')
logger.error('error message')
logger.critical('critical message')
Running this module from the command line produces the following output:
$ python simple_logging_module.py
2005-03-19 15:10:26,618 - simple_example - DEBUG - debug message
2005-03-19 15:10:26,620 - simple_example - INFO - info message
2005-03-19 15:10:26,695 - simple_example - WARNING - warn message
2005-03-19 15:10:26,697 - simple_example - ERROR - error message
2005-03-19 15:10:26,773 - simple_example - CRITICAL - critical message
The following Python module creates a logger, handler, and formatter nearly identical to those in the example listed above, with the only difference being the names of the objects:
import logging
import logging.config
logging.config.fileConfig('logging.conf')
# create logger
logger = logging.getLogger('simpleExample')
# 'application' code
logger.debug('debug message')
logger.info('info message')
logger.warning('warn message')
logger.error('error message')
logger.critical('critical message')
Aqui está o arquivo logging.conf:
[loggers]
keys=root,simpleExample
[handlers]
keys=consoleHandler
[formatters]
keys=simpleFormatter
[logger_root]
level=DEBUG
handlers=consoleHandler
[logger_simpleExample]
level=DEBUG
handlers=consoleHandler
qualname=simpleExample
propagate=0
[handler_consoleHandler]
class=StreamHandler
level=DEBUG
formatter=simpleFormatter
args=(sys.stdout,)
[formatter_simpleFormatter]
format=%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s
datefmt=
The output is nearly identical to that of the non-config-file-based example:
$ python simple_logging_config.py
2005-03-19 15:38:55,977 - simpleExample - DEBUG - debug message
2005-03-19 15:38:55,979 - simpleExample - INFO - info message
2005-03-19 15:38:56,054 - simpleExample - WARNING - warn message
2005-03-19 15:38:56,055 - simpleExample - ERROR - error message
2005-03-19 15:38:56,130 - simpleExample - CRITICAL - critical message
You can see that the config file approach has a few advantages over the Python code approach, mainly separation of configuration and code and the ability of noncoders to easily modify the logging properties.
Aviso
The fileConfig() function takes a default parameter,
disable_existing_loggers, which defaults to True for reasons of
backward compatibility. This may or may not be what you want, since it
will cause any non-root loggers existing before the fileConfig()
call to be disabled unless they (or an ancestor) are explicitly named in
the configuration. Please refer to the reference documentation for more
information, and specify False for this parameter if you wish.
The dictionary passed to dictConfig() can also specify a Boolean
value with key disable_existing_loggers, which if not specified
explicitly in the dictionary also defaults to being interpreted as
True. This leads to the logger-disabling behaviour described above,
which may not be what you want - in which case, provide the key
explicitly with a value of False.
Note that the class names referenced in config files need to be either relative
to the logging module, or absolute values which can be resolved using normal
import mechanisms. Thus, you could use either
WatchedFileHandler (relative to the logging module) or
mypackage.mymodule.MyHandler (for a class defined in package mypackage
and module mymodule, where mypackage is available on the Python import
path).
In Python 3.2, a new means of configuring logging has been introduced, using dictionaries to hold configuration information. This provides a superset of the functionality of the config-file-based approach outlined above, and is the recommended configuration method for new applications and deployments. Because a Python dictionary is used to hold configuration information, and since you can populate that dictionary using different means, you have more options for configuration. For example, you can use a configuration file in JSON format, or, if you have access to YAML processing functionality, a file in YAML format, to populate the configuration dictionary. Or, of course, you can construct the dictionary in Python code, receive it in pickled form over a socket, or use whatever approach makes sense for your application.
Here’s an example of the same configuration as above, in YAML format for the new dictionary-based approach:
version: 1
formatters:
simple:
format: '%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s'
handlers:
console:
class: logging.StreamHandler
level: DEBUG
formatter: simple
stream: ext://sys.stdout
loggers:
simpleExample:
level: DEBUG
handlers: [console]
propagate: no
root:
level: DEBUG
handlers: [console]
For more information about logging using a dictionary, see Configuration functions.
O que acontece se nenhuma configuração é fornecida¶
If no logging configuration is provided, it is possible to have a situation where a logging event needs to be output, but no handlers can be found to output the event. The behaviour of the logging package in these circumstances is dependent on the Python version.
Para versões do Python anteriores à 3.2, o comportamento é o seguinte:
If logging.raiseExceptions is
False(production mode), the event is silently dropped.If logging.raiseExceptions is
True(development mode), a message ‘No handlers could be found for logger X.Y.Z’ is printed once.
No Python 3.2 e posteriores, o comportamento é como o seguinte:
The event is output using a ‘handler of last resort’, stored in
logging.lastResort. This internal handler is not associated with any logger, and acts like aStreamHandlerwhich writes the event description message to the current value ofsys.stderr(therefore respecting any redirections which may be in effect). No formatting is done on the message - just the bare event description message is printed. The handler’s level is set toWARNING, so all events at this and greater severities will be output.
To obtain the pre-3.2 behaviour, logging.lastResort can be set to None.
Configuring Logging for a Library¶
When developing a library which uses logging, you should take care to
document how the library uses logging - for example, the names of loggers
used. Some consideration also needs to be given to its logging configuration.
If the using application does not use logging, and library code makes logging
calls, then (as described in the previous section) events of severity
WARNING and greater will be printed to sys.stderr. This is regarded as
the best default behaviour.
If for some reason you don’t want these messages printed in the absence of any logging configuration, you can attach a do-nothing handler to the top-level logger for your library. This avoids the message being printed, since a handler will always be found for the library’s events: it just doesn’t produce any output. If the library user configures logging for application use, presumably that configuration will add some handlers, and if levels are suitably configured then logging calls made in library code will send output to those handlers, as normal.
A do-nothing handler is included in the logging package:
NullHandler (since Python 3.1). An instance of this handler
could be added to the top-level logger of the logging namespace used by the
library (if you want to prevent your library’s logged events being output to
sys.stderr in the absence of logging configuration). If all logging by a
library foo is done using loggers with names matching ‘foo.x’, ‘foo.x.y’,
etc. then the code:
import logging
logging.getLogger('foo').addHandler(logging.NullHandler())
should have the desired effect. If an organisation produces a number of libraries, then the logger name specified can be ‘orgname.foo’ rather than just ‘foo’.
Nota
It is strongly advised that you do not add any handlers other
than NullHandler to your library’s loggers. This is
because the configuration of handlers is the prerogative of the application
developer who uses your library. The application developer knows their
target audience and what handlers are most appropriate for their
application: if you add handlers ‘under the hood’, you might well interfere
with their ability to carry out unit tests and deliver logs which suit their
requirements.
Níveis de Logging¶
Os valores númericos dos níveis de logging estão listados na tabela abaixo. Eles são principalmente de interesse se você quiser definir seus próprios níveis, e precisa deles para definir seus valores específicos relativos aos níveis predefinidos. Se você define um nível com o mesmo valor númerico, ele sobreescreve o valor predefinido; o nome predefinido é perdido.
Nível |
Valor numérico |
|---|---|
|
50 |
|
40 |
|
30 |
|
20 |
|
10 |
|
0 |
Levels can also be associated with loggers, being set either by the developer or through loading a saved logging configuration. When a logging method is called on a logger, the logger compares its own level with the level associated with the method call. If the logger’s level is higher than the method call’s, no logging message is actually generated. This is the basic mechanism controlling the verbosity of logging output.
Logging messages are encoded as instances of the LogRecord
class. When a logger decides to actually log an event, a
LogRecord instance is created from the logging message.
Logging messages are subjected to a dispatch mechanism through the use of
handlers, which are instances of subclasses of the Handler
class. Handlers are responsible for ensuring that a logged message (in the form
of a LogRecord) ends up in a particular location (or set of locations)
which is useful for the target audience for that message (such as end users,
support desk staff, system administrators, developers). Handlers are passed
LogRecord instances intended for particular destinations. Each logger
can have zero, one or more handlers associated with it (via the
addHandler() method of Logger). In addition to any
handlers directly associated with a logger, all handlers associated with all
ancestors of the logger are called to dispatch the message (unless the
propagate flag for a logger is set to a false value, at which point the
passing to ancestor handlers stops).
Just as for loggers, handlers can have levels associated with them. A handler’s
level acts as a filter in the same way as a logger’s level does. If a handler
decides to actually dispatch an event, the emit() method is used
to send the message to its destination. Most user-defined subclasses of
Handler will need to override this emit().
Custom Levels¶
Defining your own levels is possible, but should not be necessary, as the existing levels have been chosen on the basis of practical experience. However, if you are convinced that you need custom levels, great care should be exercised when doing this, and it is possibly a very bad idea to define custom levels if you are developing a library. That’s because if multiple library authors all define their own custom levels, there is a chance that the logging output from such multiple libraries used together will be difficult for the using developer to control and/or interpret, because a given numeric value might mean different things for different libraries.
Useful Handlers¶
Em adição à classe base Handler, muitas subclasses úteis são fornecidas:
StreamHandlerinstances send messages to streams (file-like objects).FileHandlerinstances send messages to disk files.BaseRotatingHandleris the base class for handlers that rotate log files at a certain point. It is not meant to be instantiated directly. Instead, useRotatingFileHandlerorTimedRotatingFileHandler.RotatingFileHandlerinstances send messages to disk files, with support for maximum log file sizes and log file rotation.TimedRotatingFileHandlerinstances send messages to disk files, rotating the log file at certain timed intervals.SocketHandlerinstances send messages to TCP/IP sockets. Since 3.4, Unix domain sockets are also supported.DatagramHandlerinstances send messages to UDP sockets. Since 3.4, Unix domain sockets are also supported.SMTPHandlerinstances send messages to a designated email address.SysLogHandlerinstances send messages to a Unix syslog daemon, possibly on a remote machine.NTEventLogHandlerinstances send messages to a Windows NT/2000/XP event log.MemoryHandlerinstances send messages to a buffer in memory, which is flushed whenever specific criteria are met.HTTPHandlerinstances send messages to an HTTP server using eitherGETorPOSTsemantics.WatchedFileHandlerinstances watch the file they are logging to. If the file changes, it is closed and reopened using the file name. This handler is only useful on Unix-like systems; Windows does not support the underlying mechanism used.QueueHandlerinstances send messages to a queue, such as those implemented in thequeueormultiprocessingmodules.NullHandlerinstances do nothing with error messages. They are used by library developers who want to use logging, but want to avoid the ‘No handlers could be found for logger XXX’ message which can be displayed if the library user has not configured logging. See Configuring Logging for a Library for more information.
Novo na versão 3.1: A classe NullHandler.
Novo na versão 3.2: A classe QueueHandler.
The NullHandler, StreamHandler and FileHandler
classes are defined in the core logging package. The other handlers are
defined in a sub-module, logging.handlers. (There is also another
sub-module, logging.config, for configuration functionality.)
Logged messages are formatted for presentation through instances of the
Formatter class. They are initialized with a format string suitable for
use with the % operator and a dictionary.
For formatting multiple messages in a batch, instances of
BufferingFormatter can be used. In addition to the format
string (which is applied to each message in the batch), there is provision for
header and trailer format strings.
When filtering based on logger level and/or handler level is not enough,
instances of Filter can be added to both Logger and
Handler instances (through their addFilter() method).
Before deciding to process a message further, both loggers and handlers consult
all their filters for permission. If any filter returns a false value, the
message is not processed further.
The basic Filter functionality allows filtering by specific logger
name. If this feature is used, messages sent to the named logger and its
children are allowed through the filter, and all others dropped.
Exceções levantadas durante logging¶
The logging package is designed to swallow exceptions which occur while logging in production. This is so that errors which occur while handling logging events - such as logging misconfiguration, network or other similar errors - do not cause the application using logging to terminate prematurely.
SystemExit and KeyboardInterrupt exceptions are never
swallowed. Other exceptions which occur during the emit() method
of a Handler subclass are passed to its handleError()
method.
The default implementation of handleError() in Handler
checks to see if a module-level variable, raiseExceptions, is set. If
set, a traceback is printed to sys.stderr. If not set, the exception is
swallowed.
Nota
The default value of raiseExceptions is True. This is
because during development, you typically want to be notified of any
exceptions that occur. It’s advised that you set raiseExceptions to
False for production usage.
Usando objetos arbitrários como mensagens¶
In the preceding sections and examples, it has been assumed that the message
passed when logging the event is a string. However, this is not the only
possibility. You can pass an arbitrary object as a message, and its
__str__() method will be called when the logging system needs to
convert it to a string representation. In fact, if you want to, you can avoid
computing a string representation altogether - for example, the
SocketHandler emits an event by pickling it and sending it
over the wire.
Optimização¶
Formatting of message arguments is deferred until it cannot be avoided.
However, computing the arguments passed to the logging method can also be
expensive, and you may want to avoid doing it if the logger will just throw
away your event. To decide what to do, you can call the
isEnabledFor() method which takes a level argument and returns
true if the event would be created by the Logger for that level of call.
You can write code like this:
if logger.isEnabledFor(logging.DEBUG):
logger.debug('Message with %s, %s', expensive_func1(),
expensive_func2())
so that if the logger’s threshold is set above DEBUG, the calls to
expensive_func1() and expensive_func2() are never made.
Nota
In some cases, isEnabledFor() can itself be more
expensive than you’d like (e.g. for deeply nested loggers where an explicit
level is only set high up in the logger hierarchy). In such cases (or if you
want to avoid calling a method in tight loops), you can cache the result of a
call to isEnabledFor() in a local or instance variable, and use
that instead of calling the method each time. Such a cached value would only
need to be recomputed when the logging configuration changes dynamically
while the application is running (which is not all that common).
There are other optimizations which can be made for specific applications which need more precise control over what logging information is collected. Here’s a list of things you can do to avoid processing during logging which you don’t need:
O que você não quer coletar |
How to avoid collecting it |
|---|---|
Information about where calls were made from. |
Set |
Threading information. |
Set |
Processar informação. |
Set |
Also note that the core logging module only includes the basic handlers. If
you don’t import logging.handlers and logging.config, they won’t
take up any memory.
Ver também
- Módulo
logging Referência da API para o módulo de logging.
- Módulo
logging.config API de configuração para o módulo logging.
- Módulo
logging.handlers Manipuladores úteis incluídos no módulo logging.